Structure of All Tense, Structure of the Tense.
Structure of All Tense
Tense of a sentence gives you an idea of the
time when the incident mentioned in a statement takes place. At the same time,
it is that critical factor that can most commonly leads people to mistakes
while framing a sentence or while identifying the time of events. With your
knowledge of tenses strong, fluent English and flawless grammar isn't too far
away from you. Here, in this article, all the various types of tenses are
explained, along with their structure and examples, to help you get a much
clearer picture of this important part of speech; it would also provide you the
confidence to pick the right type of tense. Though it might seem complicated
when you try to glance through the write-up, tenses aren't that difficult to
understand; spend some time on each tense mentioned and see yourself framing
better sentences than before. Read the following section carefully. The
examples mentioned below can guide you through for sure.
Tenses In English
Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
A sentence is presented in simple present tense when it is used to describe an action that's happening at present and does not indicate when the action is expected to end. Simple present tense is used when:
Tenses In English
Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
A sentence is presented in simple present tense when it is used to describe an action that's happening at present and does not indicate when the action is expected to end. Simple present tense is used when:
- The action that is taking place
in general.
- The action is not only
occurring now; it repeats after regular intervals of time.
- To indicate facts those are
generally true.
- The action for relating habits
and routines that happen all the time, be it in the future, past or
present.
Structure:
Verb "+s/es" form is used;
Verb "+s/es" form is used;
- If subject is 3rd person
singular.
The verb is used in its original form; - If subject is 1st and/or 2nd
person singular.
- If subject is 1st and/or 2nd
person plural.
- If subject is 3rd person
plural.
Some Examples:
- The sun sets in
the west.
- All the cars stop at
this crossing.
- Michael teaches social
studies in a school.
- That notice reads,
“No parking”.
- Rajdhani leaves at
seven in the morning.
- The teacher said if she works hard
she will pass.
- There goes the
taxi.
- Do you
play tennis?
- He does not go
to the temple.
- Does he
write novels?
Present Progressive Or Present Continuous
Though the simple present and present continuous tenses are used interchangeably, present continuous usually defines an act that is going on at the time of speaking.
The sentences with present progressive tense are used when:
Though the simple present and present continuous tenses are used interchangeably, present continuous usually defines an act that is going on at the time of speaking.
The sentences with present progressive tense are used when:
- Something is taking place now,
while speaking and has a definite end as well.
- When something is already
decided and arranged as well to perform it.
- To indicate an undesirable
habit.
Structure:
- Use first form of the verb
“+ing”
- Singular 3rd person subject —
use ‘is’
- Plural 1st, 2nd and 3rd person
and singular 2nd person subject — use ‘are’
- 1st person singular — use ‘am’
In other words, it is "Subject + be (is,
am, are) + Verb+ -ing + Object"
Some Examples:
Some Examples:
- Please wait for a moment, Shyam
is talking to Mary.
- We are late; he will be waiting for
us at the restaurant now.
- Mom, I am playing football.
- Are they still living here?
- She is having her
breakfast now.
- I’m planning to
meet the Director tonight.
Present Perfect Tense
It's probably the most used tense form in English Grammar and is also considered difficult to understand. The Present Perfect Tense explains the incident that has happened in the past and that continues until the present time.
Examples
It's probably the most used tense form in English Grammar and is also considered difficult to understand. The Present Perfect Tense explains the incident that has happened in the past and that continues until the present time.
Examples
- For almost five generations, my
family members have been engineers.
- In order to avoid delays in my
work, I have been doing it regularly.
- I have always
wanted to ride on this vehicle.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Usually, Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for a situation that has occurred in the past and which continues until that moment.
Structure:
Usually, Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for a situation that has occurred in the past and which continues until that moment.
Structure:
- Use the first form of the verb
+ “–ing”
- Singular subject (has been),
Plural subject or I (have been)
- ‘Since’— if the point of time
is mentioned.
- ‘For’ — if the duration of time
is specified.
Examples:
- I have been eating apples
today.
- You have not been
studying for the past month.
- We haven’t been playing with
Mary since Tuesday.
Past Tense
Simple Past Tense
Simple past tense is used to narrate an action of the past. The verb in the past tense ends with an '-ed' and hence, there are seven ways of marking the irregular verbs in the past tense. The most common being the change of the vowel as in 'drink' - 'drank'.
Construction
Subject + verb + Object
Examples:
Simple Past Tense
Simple past tense is used to narrate an action of the past. The verb in the past tense ends with an '-ed' and hence, there are seven ways of marking the irregular verbs in the past tense. The most common being the change of the vowel as in 'drink' - 'drank'.
Construction
Subject + verb + Object
Examples:
- Katie worked in
that office for almost four years.
- He passed away
in 1999.
- We went for
the movie yesterday.
- Three years ago, I studied at
the Canada University.
Past Continuous Tense
This from of tense indicates activities that have already happened in the past and have been completed before the time of mention. These sentences are formed with the help of an auxiliary verb and giving the main verb an 'ing' ending.
Structure
Subject + was/were + Verb in its -ing form + Object
Examples:
This from of tense indicates activities that have already happened in the past and have been completed before the time of mention. These sentences are formed with the help of an auxiliary verb and giving the main verb an 'ing' ending.
Structure
Subject + was/were + Verb in its -ing form + Object
Examples:
- He was washing the
dishes, while she was cooking dinner.
- I was working at
11p.m yesterday.
- We were playing football
when it started to rain.
- She was reading a
thriller novel when I called her.
- What were you doing when
Sam arrived?
- I was walking down
the street yesterday when the police van was patrolling the
city.
Past Perfect Tense
This tense refers to a non-continuous action that was already completed in the past. Such sentences are formed by using the Simple Past form of the auxiliary verb 'to have', followed by the past participle form of the verb.
Structure
Subject + had + past participle form of verb + Object
Example:
This tense refers to a non-continuous action that was already completed in the past. Such sentences are formed by using the Simple Past form of the auxiliary verb 'to have', followed by the past participle form of the verb.
Structure
Subject + had + past participle form of verb + Object
Example:
- I had never seen such
a beautiful before.
- She understood the movie only
because she had read the book.
- Clara had never been to
a club before last night.
- We didn’t get a room in the
hotel because we had not booked in advance.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
A continuous action that was completed sometime in the past falls under Past Perfect Continuous tense. Such sentences are framed by using the modal, 'had' + 'been' + the present participle of the verb (-ing).
Structure:
Subject + had + been + Verb (ing) + object
Example:
A continuous action that was completed sometime in the past falls under Past Perfect Continuous tense. Such sentences are framed by using the modal, 'had' + 'been' + the present participle of the verb (-ing).
Structure:
Subject + had + been + Verb (ing) + object
Example:
- I had been playing the
guitar all morning.
- I had been sleeping all
the way from the beginning of the class.
- He had been trying to
call her.
- Until this year, Neha had
been going to a village school.
- The baby had been
crying out loud for minutes when her mother fed her.
Future Tense
Simple Future Tense
This tense is used for those sentences which refer to the actions which will occur later, in future. This requires a future tense auxiliary verb even though the verb would be unmarked.
Examples:
Simple Future Tense
This tense is used for those sentences which refer to the actions which will occur later, in future. This requires a future tense auxiliary verb even though the verb would be unmarked.
Examples:
- You will be
done before me.
- She will not
come tomorrow.
- Will you
come to play with me after school?
- I will keep in
touch with you.
- I will reach
home by 7p.m.
- He will stay
with us for 3 days.
Future Continuous Tense
This tense defines those acts which will be continued at a future point of time. In order to form a future continuous tense sentence, a future auxiliary verb is required followed by a main verb that ends with -ing.
Structure:
'will' + 'be' + present participle of the verb (ing).
Construction
This tense defines those acts which will be continued at a future point of time. In order to form a future continuous tense sentence, a future auxiliary verb is required followed by a main verb that ends with -ing.
Structure:
'will' + 'be' + present participle of the verb (ing).
Construction
- Use first form of the verb
(+ing)
- 1st and 2nd person — ‘Shall be’
- 3rd person — ‘Will be’
However, nowadays this distinction of 'will'
and 'shall' is not followed. Instead, 'will' is used wherever absolute
conviction is required to be expressed while the usage of 'shall' depends on
individual writing style.
Examples:
Examples:
- We assume that our
representative will be winning the elections that are to
be held at the end of April.
- Today, she will be walking all
the way to her house from her office.
- I will be watching the
new movie next week.
- By this time tomorrow, I will
be at home watching T.V.
Future Perfect Tense
This tense is used to express an act that is predicted to be finished within a certain span of time in the future. Such sentences are formed by 'will' + 'have' + 'past participle of the verb'.
Examples:
This tense is used to express an act that is predicted to be finished within a certain span of time in the future. Such sentences are formed by 'will' + 'have' + 'past participle of the verb'.
Examples:
- By the end of the year, he will
have saved enough for his sister’s wedding.
- You will have left for
London by the time this bridge gets renewed.
- Calvin will have gone by
the time you reach there by bus.
- I will have walked 15
kms by this time.
- How long will it have
been since we were here together?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
This tense form indicates an action that is continuous and, at some point in the future, it will be completed. It is formed using the modal 'will/shall' + 'have' + 'been' + 'the past participle of the verb (-ing)'.
Examples:
This tense form indicates an action that is continuous and, at some point in the future, it will be completed. It is formed using the modal 'will/shall' + 'have' + 'been' + 'the past participle of the verb (-ing)'.
Examples:
- Next Saturday, I will
have been working on this assignment for three years.
- Tomorrow, at this time, I shall
have been playing cricket since morning.
- I will have been
studying English for two hours by the time you arrive here.
Tenses are critical to sensible and flawless
language. They help you convey your ideas clearly by way of words. They help
indicate the time of the statement and provide the reader with a crystal-clear
picture of incidents. With mere practice, you will be able to grab all the
concepts of the correct usage of the tenses.
Related page
What is Tense? Definition of Tense.
What is the type of tense?
What Is the Past Tense?
What Is the Present Tense?
What is the Future Tense?
Structure of All Tense
Simple Present Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Past Tense
Past Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Future Tense
Future Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
All Tense with example
Table of English Tenses with example
TENSE CHART
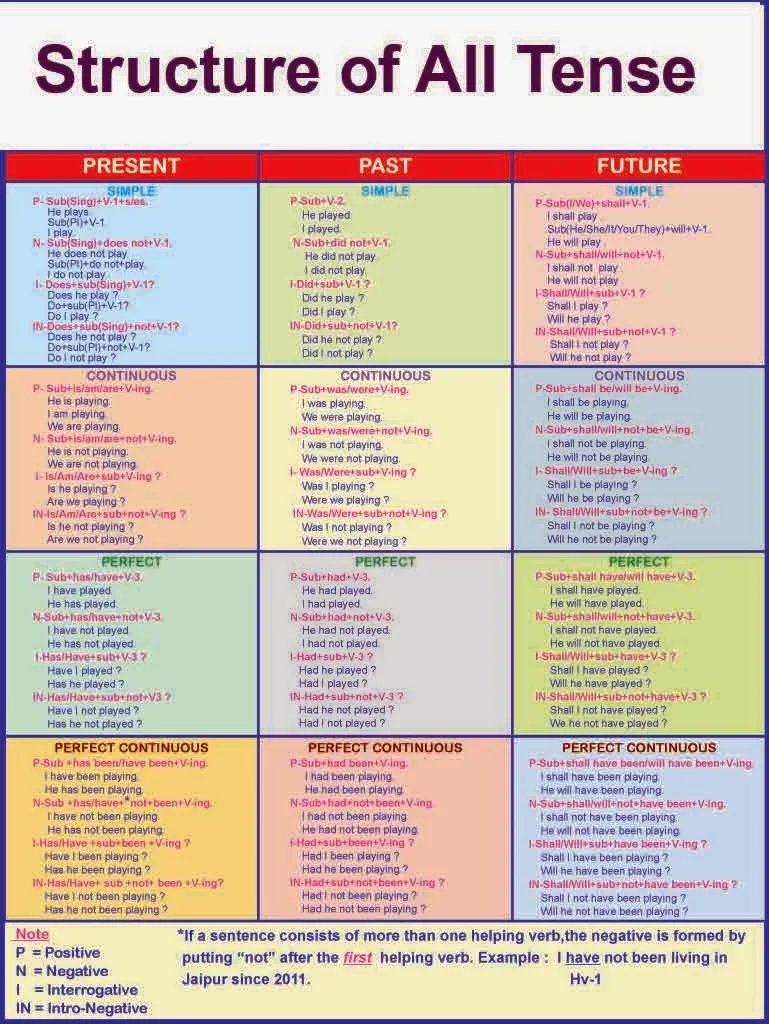




A great picture for learning about tenses :D
ReplyDeleteThis website has a video and more great pictures like this 2 www.learningenglishvocabularygrammar.com/grammar/grammar-pdf/12-verb-tenses-english-grammar
Wonderful
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteKerala SSLC Time Table 2018
ReplyDeletePSEB 12th Date Sheet 2018
IBPS PO Mains Result 2017
BTER Jodhpur Revaluation Form 2017
UPBTE Result 2017
good but the pics are not clear
ReplyDeleteyah
ReplyDeleteThank you for imparting this remarkable piece of detail here. I am sure that this might benefit numerous visitors of the blog. Great work, keep it up!
ReplyDeleteEnglish Practice App | English Learning App
Such a useful and informative article. Each and every tense explained properly.Keep up the good work. Chandigarh
ReplyDeleteGreat job on posting a helpful article known with The Parts of Speech. i'm likewise poring over all of your alternative journal entries too. i favor investigation articles on isolated subjects. i'm super beguiled and can survey your web site all around. enthralling articles on your web site legitimizes the intrigue. this can be a astounding piece of labor. I magnificently welcome the standard structure on this web site.
ReplyDeletevery useful but picture is unclear
ReplyDeleteIts vry useful ..... But the first is not clear
ReplyDeleteIts vry useful ..... But the first is not clear
ReplyDeleteYou have just sent me what I was just going to look for. Did you read my mind?
ReplyDeletePhotos clear nhi aa rha hai
ReplyDeletePhoto quality badaye
ReplyDeleteGreat job....❤
ReplyDeleteSir would u like to sand me on my G mail account that the 1st picture is,nt clear i want these structure of all tenses .....!
ReplyDeleteVery useful
ReplyDeleteNice but post pic clearly and also add download button plz
ReplyDeleteThank you very much for this awesome channel . Your knowledge and expertise really helped me out . It is clear your put so much time and hard work into preparing this presentation. You’re write up really help me organize my thoughts on topic of Types of Sentences . I really appreciate .
ReplyDeleteIt was very usefull for me. Great job👌👍
ReplyDeleteThanks a lot.
ReplyDeleteIt’s nice to use.
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteThanks very much it was very usefully me. but post pic don't clearly.
ReplyDeleteIt is very very important to us. God bless you.
ReplyDeleteGreat work but the image quality is not ok
ReplyDelete