Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is used for events that happened or started and completed in the past and that have no relation with the present. The past form of the verb is the same for all persons and things regardless of whether they are singular or plural. If the verb is a regular verb, it takes the base form of the verb with –ed added (kick – kicked) or –d added (bake - baked) if it ends in –e.
We use the simple past tense:
to describe an action that occurred in the past or at a specified time or the time is easily understood or already implied.
Examples:
- My grandfather played for the Golden Hornless Bull football team.
- I ate a big spicy piece of pizza for my breakfast.
- We finished our final exam an hour ago.
Not: We have/had finished our final exam an hour ago..
to refer to an action completed regardless of how recent or distant in the past.
Examples:
- My brother joined the circus as a clown last week..
- Alexander Bell invented the telephone in 1876.
- The police recaptured the escaped prisoner three months later.
for an action done repeatedly, habitually or at regular times in the past.
Examples:
- He visited his mother every Sunday until her death.
- We saw the movie 'Titanic' several times at the cinema.
- Brian was always a heavy drinker in the old days.
for a state in the past.
Examples:
- I felt very tired after a couple of games of tennis.
- My poor mother had backache for nearly a year.
for a short event or action that comes or follows one after the other.
Examples:
- We looked left and we looked right. Then we crossed the road.
- We followed the path, then turned left into another path, and lost our way.
to talk about someone who has died.
Examples:
- Arthur was a highly respected science-fiction writer.
- He left all his money to me.
in providing details or information that follow news reports which, when first reported, are usually expressed in present perfect tense.
Examples:
- Negotiations with the insurgent forces have broken down. The leader of the insurgent forces blamed the government for the break down. A government spokesman said the insurgent forces made unreasonable demands.
To ask a question, the past tense of the auxiliary verb do, which is did, is the only word used, whether the subject in the question is a singular or plural noun, or a singular or plural pronoun.
Examples:
- He visited his mother every Sunday until her death.
- Did your boss give you a lift home?
- Did the mosquitoes keep you awake the whole night?
- Did he promise you he would not tell anyone about it?
- Did they agree among themselves?
What Is the Simple Past Tense? (with Examples)
The simple past tense is used to describe a completed activity that happened in the past. In other words, it started in the past and ended in the past.
Uses of the Simple Past Tense
Here are some examples of the simple past tense (shaded):
- The Martians landed near the aqueduct.
- The burglar considered using the fire escape.
Of course, you can also have the negative version, which is formed "did not" + "[verb in base form]":
- The Martians did not land near the aqueduct.
- The burglar did not consider using the fire escape.
(We could have used didn't instead of did not.)
And the question versions:
- Did the Martians land near the aqueduct?
- Why didn't the burglar consider using the fire escape?
Forming the Simple Past Tense
Here is an infographic explaining the simple past tense:
The Simple Past Tense with Time Expressions
The simple past tense is often seen with a time expression explaining when the activity took place or how long it lasted.
Examples of "when an activity took place":
- On Tuesday last week, the Martians landed near the aqueduct.
("On Tuesday last week" tells you when it happened. It's called an adverbial phrase of time. Other examples are"Yesterday," "Last year," "Before breakfast,". They are really common. When any adverb appears at the front of a sentence, it is usual to follow it with a comma. A comma is not usually used when the adverbial phrase appears at the back of a sentence. NB: This is not a strict rule. Use a comma if it helps your reader.)
Read more about commas with adverbial phrases.
- The Martians landed near the aqueduct on Tuesday last week.
- Just before he was caught, the burglar considered using the fire escape.
(Note: No comma)
("Just before he was caught" tells you when the activity took place.)
Examples of "how long an activity took":
- Last week, the council inspected the drains.
- Her daughter hid under the bed for three hours.
("Last week" tells you when it happened and for how long.)
(Using "for" is a common way of describing how long an activity lasted.)
The Simple Past Tense
Verbs have different forms, called tenses. The tense of a verb tells us when the action happens.
We use the simple past tense to talk about things that happened in the past.
Examples:
The children visited the zoo last week.
The plane landed a few minutes ago.
Jerry dried his clothes in the sun.
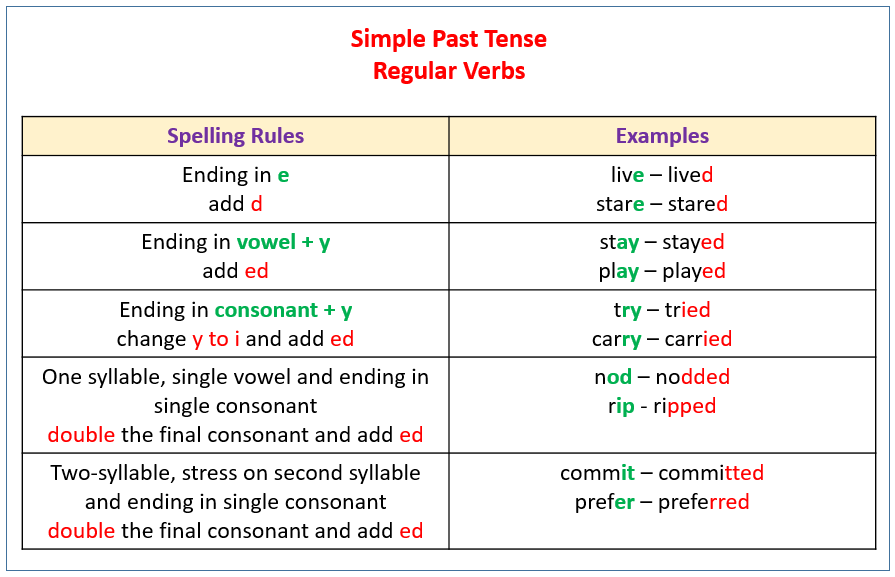
Regular Verbs
For most verbs, the simple past tense is created by adding a d, ed or ied at the end of the word. These are called regular verbs. There are also irregular verbs which do not follow this pattern.
The following are some of the rules for regular verbs.
For verbs ending in e add a d.
Example:
Present Tense | Past Tense |
live | lived |
love | loved |
date | dated |
agree | agreed |
die | died |
queue | queued |
stare | stared |
invite | invited |
The simple past tense of some verbs do not end in ed. Such verbs are called irregular verbs. Since they are irregular, they do not follow any pattern and the best way to learn them would be to repeat and memorize them.
Usually we will try to remember the base form (infinitive), past tense and past participle.
Examples:
They go to the movies every weekend. (go - base form)
They went to the movie yesterday. (went - past tense)
They have gone to the movies. (gone - past participle)
The following is a list of commonly used irregular verbs. (Check out the videos below for more irregular verbs.)
Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
arise | arose | arisen |
awake | awoke | awoken |
be | was, were | been |
bear | bore | born/borne |
beat | beat | beaten |
become | became | become |
begin | began | begun |
behold | beheld | beheld |
bend | bent | bent |
bet | bet | bet |
bid | bade | bidden |
bid | bid | bid |
bind | bound | bound |
bite | bit | bitten |
bleed | bled | bled |
blow | blew | blown |
break | broke | broken |
breed | bred | bred |
bring | brought | brought |
build | built | built |
burst | burst | burst |
bust | bust | bust |
buy | bought | bought |
cast | cast | cast |
catch | caught | caught |
choose | chose | chosen |
clap | clapped | clapped |
cling | clung | clung |
come | came | come |
cost | cost | cost |
creep | crept | crept |
cut | cut | cut |
dare | dared | dared |
deal | dealt | dealt |
dig | dug | dug |
dive | dived | dived |
do | did | done |
draw | drew | drawn |
dream | dreamt | dreamt |
drink | drank | drunk |
drive | drove | driven |
dwell | dwelt | dwelt |
eat | ate | eaten |
fall | fell | fallen |
feed | fed | fed |
feel | felt | felt |
fight | fought | fought |
find | found | found |
flee | fled | fled |
fling | flung | flung |
fly | flew | flown |
forbid | forbade | forbidden |
foresee | foresaw | foreseen |
foretell | foretold | foretold |
forget | forgot | forgotten |
forgive | forgave | forgiven |
forsake | forsook | forsaken |
freeze | froze | frozen |
frostbite | frostbit | frostbitten |
get | got | gotten |
give | gave | given |
go | went | gone |
go | went | gone/been |
grind | ground | ground |
grow | grew | grown |
handwrite | handwrote | handwritten |
have | had | had |
hear | heard | heard |
hide | hid | hidden |
hit | hit | hit |
hold | held | held |
hurt | hurt | hurt |
inlay | inlaid | inlaid |
input | input | input |
interlay | interlaid | interlaid |
keep | kept | kept |
kneel | knelt | knelt |
know | knew | known |
lay | laid | laid |
lead | led | led |
learn | learnt | learnt |
leave | left | left |
lend | lent | lent |
let | let | let |
lie | lay | lain |
light | lit | lit |
lose | lost | lost |
make | made | made |
mean | meant | meant |
meet | met | met |
pay | paid | paid |
quit | quit | quit |
read | read | read |
ride | rode | ridden |
run | ran | run |
say | said | said |
see | saw | seen |
seek | sought | sought |
sell | sold | sold |
send | sent | sent |
shake | shook | shaken |
shine | shone | shone |
sing | sang | sung |
sit | sat | sat |
sleep | slept | slept |
speak | spoke | spoken |
spend | spent | spent |
spring | sprang | sprung |
stand | stood | stood |
steal | stole | stolen |
swim | swam | swum |
swing | swung | swung |
take | took | taken |
teach | taught | taught |
tear | tore | torn |
tell | told | told |
think | thought | thought |
throw | threw | thrown |
understand | understood | understood |
wake | woke | woken |
wear | wore | worn |
win | won | won |
write | wrote | written |



No comments